In order to utilize bidirectional charging, installation of a bidirectional EV charger is required. This type of charging has the capability to power a single load, act as a backup battery for a household or even return energy to the grid. In contrast, traditional EV chargers are only equipped to send power in one direction (i.e. to charge a car's battery), while a bidirectional charger is designed to send power in both directions.
Bidirectional electric vehicle chargers may come equipped with a DC to AC inverter, enabling bidirectional charging. These chargers harness DC power reserves from the vehicle's battery and convert it into AC electricity for household use., for example.
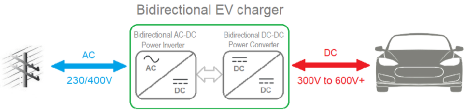
Bidirectional EV Charger - Source: Clean Energy Reviews
What Is Bidirectional EV Charging and How Does It Work?
Currently, the vast majority of electric vehicles (EVs) utilize unidirectional charging, which involves taking alternating current (AC) electricity from the grid and converting it to direct current (DC) to charge the car's battery. Conversely, bidirectional charging provides a two-way flow of electricity: the grid can supply power to charge the EV, or the EV can transfer power back into the grid a home office building or household appliance. However, bidirectional charging requires DC power to be converted back to AC using a specialized system.
V2X electric car charging technology gives EV drivers access to different bidirectional charging applications. The “X” in V2X is a reference to each use:
G: Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
H: Vehicle-to-Home (V2H)
V: Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V)
L: Vehicle-to-Load (V2L)
B: Vehicle-to-Building (V2B)
It is important to note that not all bidirectional EVs are designed for every V2X application. In this section, we explain the different V2X applications.
V2G, V2H, V2L: What’s the Difference?
As the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) increases, bidirectional charging technology allows for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) charging. V2G aims to provide significant amounts of electricity from EV batteries in order to balance energy demands ,This technology also allows for energy optimization based on utility costs and time of day . For instance, during times of peak energy usage EVs can return power to the grid while they can be charged during off-peak times, resulting in reduced costs.
While the vehicle is stationary, V2H technology extracts energy directly from its battery and redirects it towards powering a nearby home or building. This innovative solution not only helps to reduce the demand on the power grid, but can also serve as a reliable backup in the event of a power outage. Additionally, V2H presents an opportunity for significant cost savings by allowing the EV to provide electricity to the home during peak hours when utility rates are typically at their highest.
A third category of charging, known as vehicle-to-load (V2L), enables electric vehicles to supply AC power to charge household appliances and large electronic devices. Unlike the previous methods, V2L does not necessitate a dedicated bidirectional charger and instead uses an integrated inverter to transmit power to the device. It is worth noting that V2L represents a promising technology for the future of electric vehicle charging, as it allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in the use of electric vehicles.
the potential of bidirectional charging will be fully realized in the near future with an increase in the number of electric vehicles equipped with this technology and improved infrastructure that can effectively support it.
Knowing the basic issues associated with bidirectional charging can help to simplify the selection process of these components. By working with an experienced power supply company, such as Landworld, the effort required to complete the selection process can be minimized, and optimal bidirectional charging product can be identified.



 Previous
Previous Next
Next Return
Return